Service Discovery is one of the core building blocks in microservices architecture. It ensures that services can find and communicate with each other dynamically — without hard-coding IP addresses.
Below is a very clear explanation with visuals and examples. 👇
🚀 How to Manage Service Discovery in Microservices



⭐ Why do we need Service Discovery?
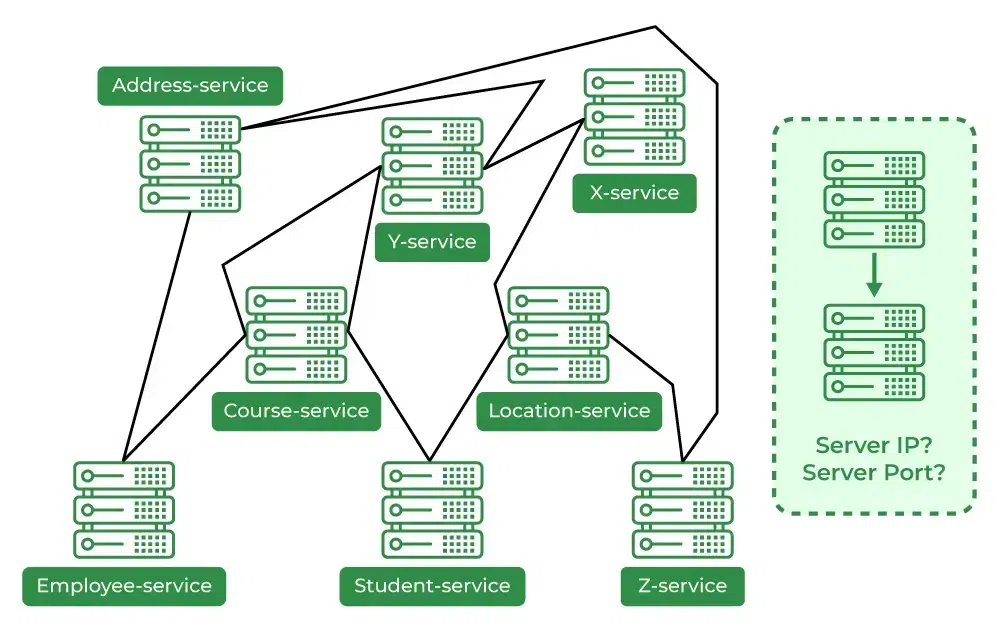
In microservices:
-
Instances scale up/down dynamically
-
IPs change frequently (containers restart)
-
Hardcoding URLs breaks the system
Service discovery solves this by letting services register themselves and discover others.
👉 Two Types of Service Discovery
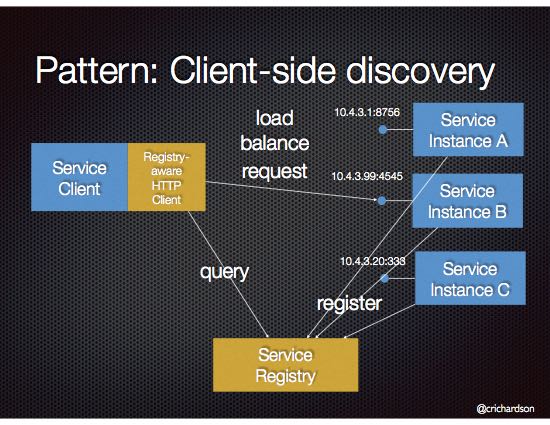
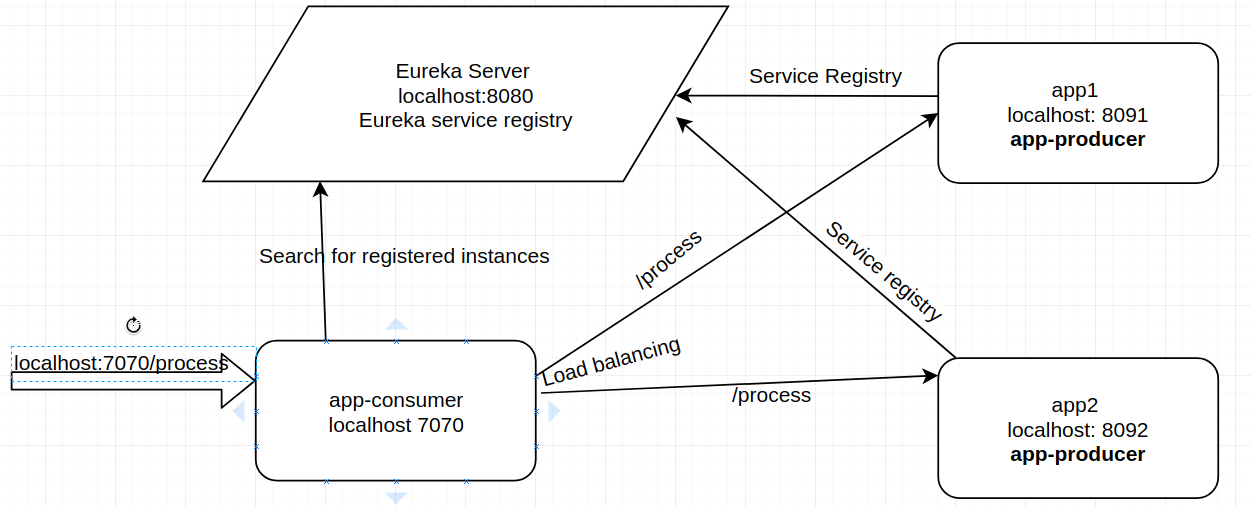
1. Client-Side Discovery
Here clients find service locations themselves using a Service Registry.
📌 Workflow:
-
Service registers with a registry (Eureka, Consul).
-
Client asks registry for location.
-
Client calls the service directly.
Example:
-
Netflix Eureka
-
Ribbon/Feign (load balancer)
Diagram:
Java (Spring Cloud) Example:
@FeignClient(name = "payment-service")
public interface PaymentClient {
@GetMapping("/pay")
String makePayment();
}
Here, "payment-service" is fetched dynamically from Eureka.
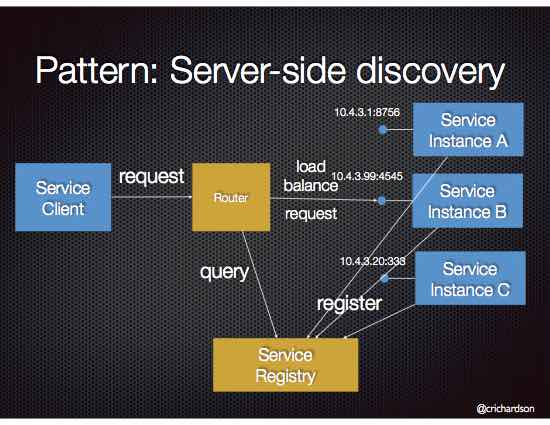
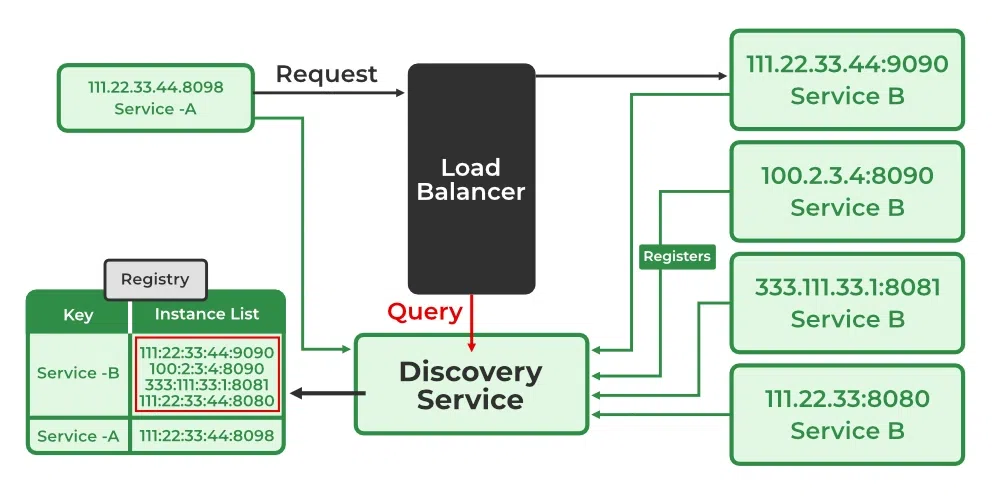
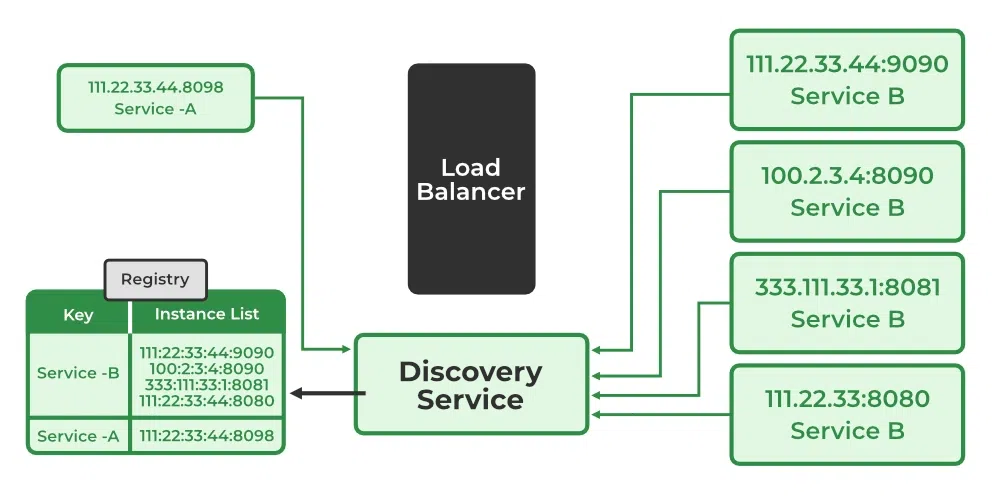
2. Server-Side Discovery
Here the API Gateway / Load Balancer discovers the service.
📌 Workflow:
-
Services register with registry.
-
Client calls API Gateway.
-
Gateway queries registry.
-
Gateway routes request to the correct service.
Technologies:
-
AWS ALB
-
NGINX + Consul
-
Kubernetes (Kube-DNS / CoreDNS)
Diagram:

🛠 Popular Tools for Service Discovery
1️⃣ Netflix Eureka (Most common for Java/Spring Boot)
-
Lightweight
-
Easy integration with Spring Cloud
-
Client-side discovery
Example in Spring Boot:
@EnableEurekaClient
@SpringBootApplication
public class OrderServiceApplication { }
2️⃣ Consul
-
Health checks
-
Key-value store
-
Multi-language
-
Used with API gateway (Traefik, Envoy)
3️⃣ Kubernetes Native Service Discovery
In Kubernetes, service discovery is built-in.
-
Uses DNS-based discovery
-
Each service gets a stable DNS name:
payment-service.default.svc.cluster.local
Kubernetes automatically updates service endpoints as pods scale.
📘 How Service Discovery Works (Simple Steps)
-
Service Registers
-
Automatically through Spring Cloud / Consul agent / K8s service.
-
-
Health Checks
-
Registry removes unhealthy instances.
-
-
Service Lookup
-
Client or gateway resolves the target service.
-
-
Load Balancing
-
Client-side (Ribbon) or server-side (Gateway).
-
🎯 Best Practices
✔ Use heartbeats to maintain registry freshness
✔ Use API Gateway + server-side discovery for external clients
✔ Use Eureka for Spring Boot monolith-to-microservices migration
✔ Use Kubernetes if deploying on containers
✔ Always enable health checks
✔ Avoid hardcoding service URLs
💡 Want architecture diagrams?
I can create for you:
-
High-level service discovery architecture
-
Eureka + API Gateway flow with arrows
-
Microservices deployment in AWS / Kubernetes
Just tell me what diagram you want.
No comments:
Post a Comment